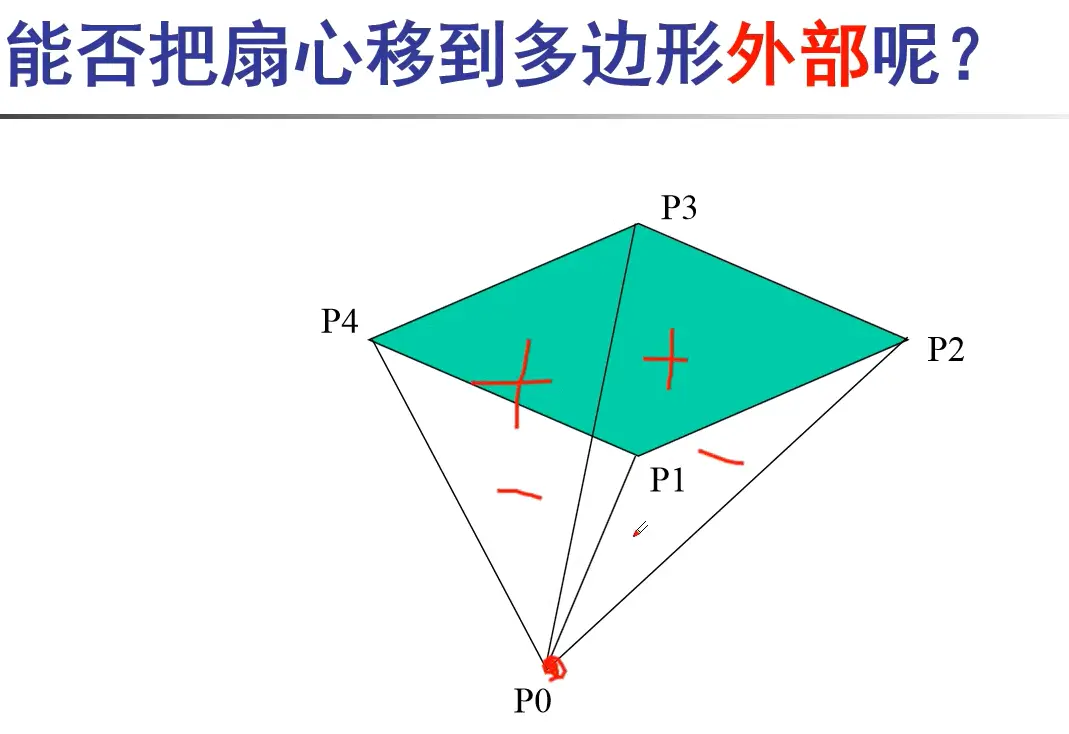
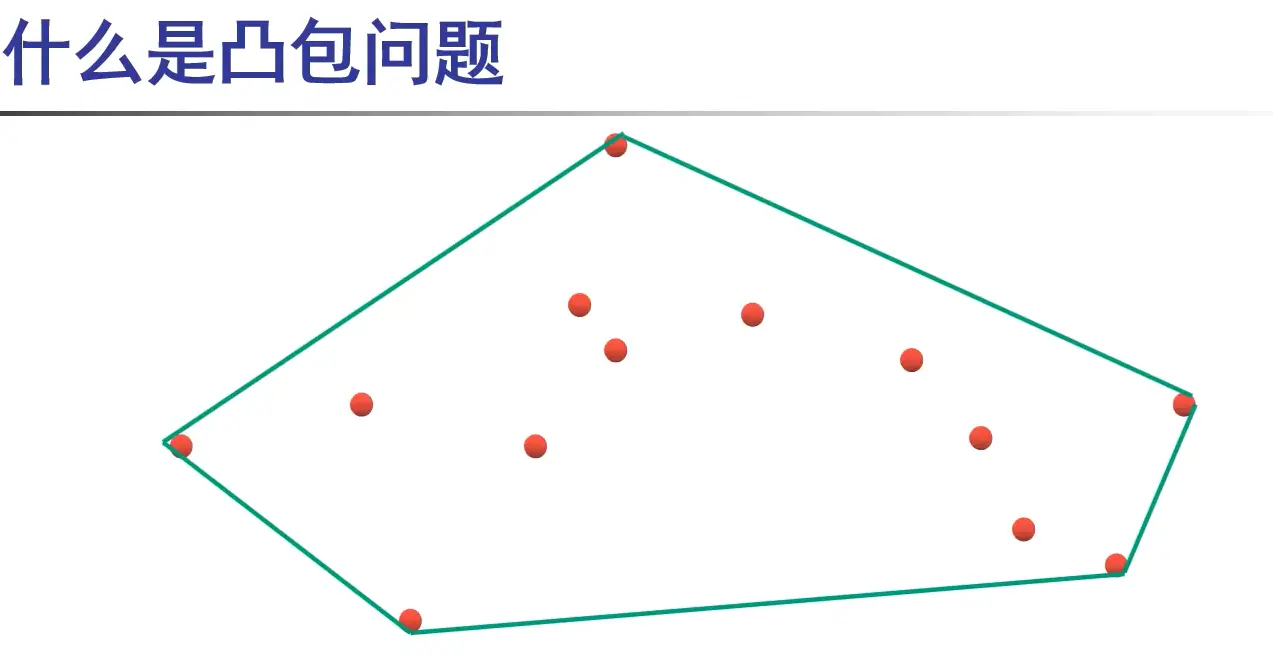
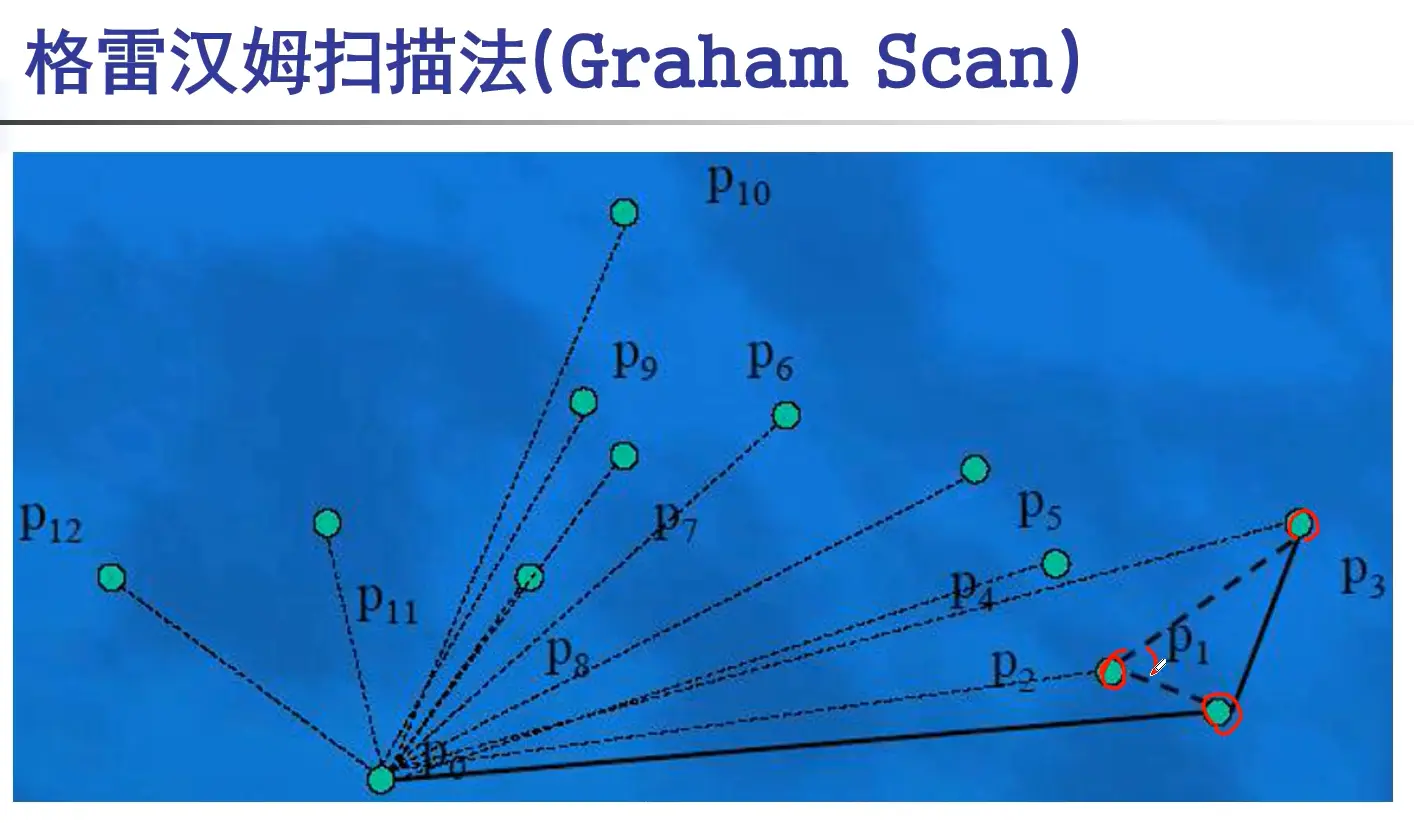
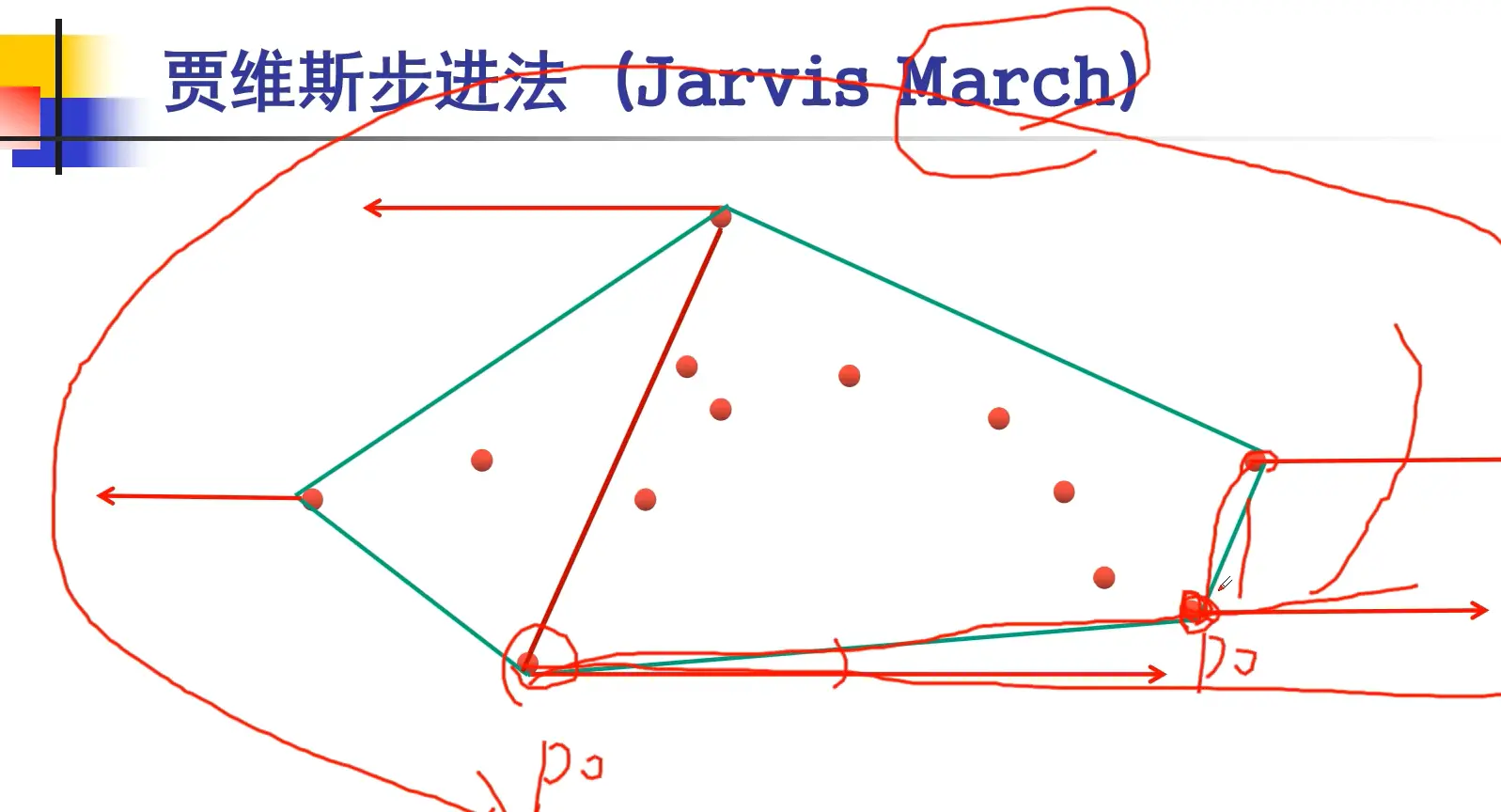
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
int sign(ll x){
if(x>0){
return 1;
}
else if(x<0){
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
struct frac{
ll z;
ll m;
ll gcd(ll a,ll b){
while(b){
ll r=a%b;
a=b;
b=r;
}
return a;
}
void create(ll a,ll b=1){
ll t=gcd(a,b);
z=a/t;
m=b/t;
if(m<0){
m=-m; z=-z;
}
}
void print(){
if(m==1){
printf("%lld",z);
}
else{
printf("%lld/%lld",z,m);
}
}
};
struct point{
ll x;
ll y;
bool operator ==(const point &p){
return x==p.x && y==p.y;
}
ll cross(const point &p1,const point &p2){
return (p1.x-x)*(p2.y-y)-(p2.x-x)*(p1.y-y);
}
};
struct segment{
point s;
point t;
bool ispoint(){
return s==t;
}
ll cross(point &p){
return p.cross(s,t);
}
bool has(point &p){
if(cross(p)!=0){
return false;
}
if(s.x==t.x){
return p.y<=max(s.y, t.y)
&& p.y >= min(s.y, t.y);
}
else{
return p.x <= max(s.x, t.x)
&& p.x >= min(s.x, t.x);
}
}
bool operator ==(const segment &seg){
return (s==seg.s && t==seg.t) (s==seg.t && t==seg.s);
}
};
int intersection(segment &p1, segment &p2, frac &x, frac &y){
bool isp1=p1.ispoint();
bool isp2=p2.ispoint();
if(isp1 && isp2){
if(p1==p2){
x.create(p1.s.x);
y.create(p1.s.y);
return 1;
}
else{
return 0;
}
}
else if(isp1 isp2){
if(isp1 && p2.has(p1.s)){
x.create(p1.s.x);
y.create(p1.s.y);
return 1;
}
else if(isp2 && p1.has(p2.s)){
x.create(p2.s.x);
y.create(p2.s.y);
return 1;
}
else
return 0;
}
else{
ll a,b,c,d;
int s1,s2,s3,s4;
s1 = sign(a = p2.cross(p1.s));
s2 = sign(b = p2.cross(p1.t));
s3 = sign(c = p1.cross(p2.s));
s4 = sign(d = p1.cross(p2.t));
if((s1^s2) == -2 && (s3 ^ s4) == -2){
x.create(b*p1.s.x - a*p1.t.x, b-a);
y.create(b*p1.s.y - a*p1.t.y, b-a);
return 1;
}
else if(a==0 && b==0){
if(p2.has(p1.s) && p2.has(p1.t)){
return -1;
}
else if(p2.has(p1.s)){
if((p1.s==p2.s && !p1.has(p2.t))
(p1.s==p2.t && !p1.has(p2.s))){
x.create(p1.s.x);
y.create(p1.s.y);
return 1;
}
else
return -1;
}
else if(p2.has(p1.t)){
if((p1.t==p2.t && !p1.has(p2.s) )
(p1.t == p2.s && !p1.has(p2.t) )){
x.create(p1.t.x);
y.create(p1.t.y);
return 1;
}
else{
return -1;
}
}
else{
if(p1.has(p2.s)){
return -1;
}
else{
return 0;
}
}
}
else if(a==0){
if(p2.has(p1.s)){
x.create(p1.s.x);
y.create(p1.s.y);
return 1;
}
else{
return 0;
}
}
else if(b==0){
if(p2.has(p1.t)){
x.create(p1.t.x);
y.create(p1.t.y);
return 1;
}
else{
return 0;
}
}
else if(c==0){
if(p1.has(p2.s)){
x.create(p2.s.x);
y.create(p2.s.y);
return 1;
}
else{
return 0;
}
}
else if(d==0){
if(p1.has(p2.t)){
x.create(p2.t.x);
y.create(p2.t.y);
return 1;
}
else {
return 0;
}
}
else{
return 0;
}
}
}
int main(){
int t;
cin>>t;
frac x,y;
int flag=0;
segment ab,cd;
while(t--){
scanf("%lld %lld %lld %lld",&ab.s.x,&ab.s.y,&ab.t.x,&ab.t.y);
scanf("%lld %lld %lld %lld",&cd.s.x,&cd.s.y,&cd.t.x,&cd.t.y);
flag= intersection(ab,cd,x,y);
if(flag==1){
printf("1\n");
x.print(),printf(" "),y.print();
printf("\n");
}
else if(flag==0){
printf("0\n");
}
else {
printf("INF\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
|
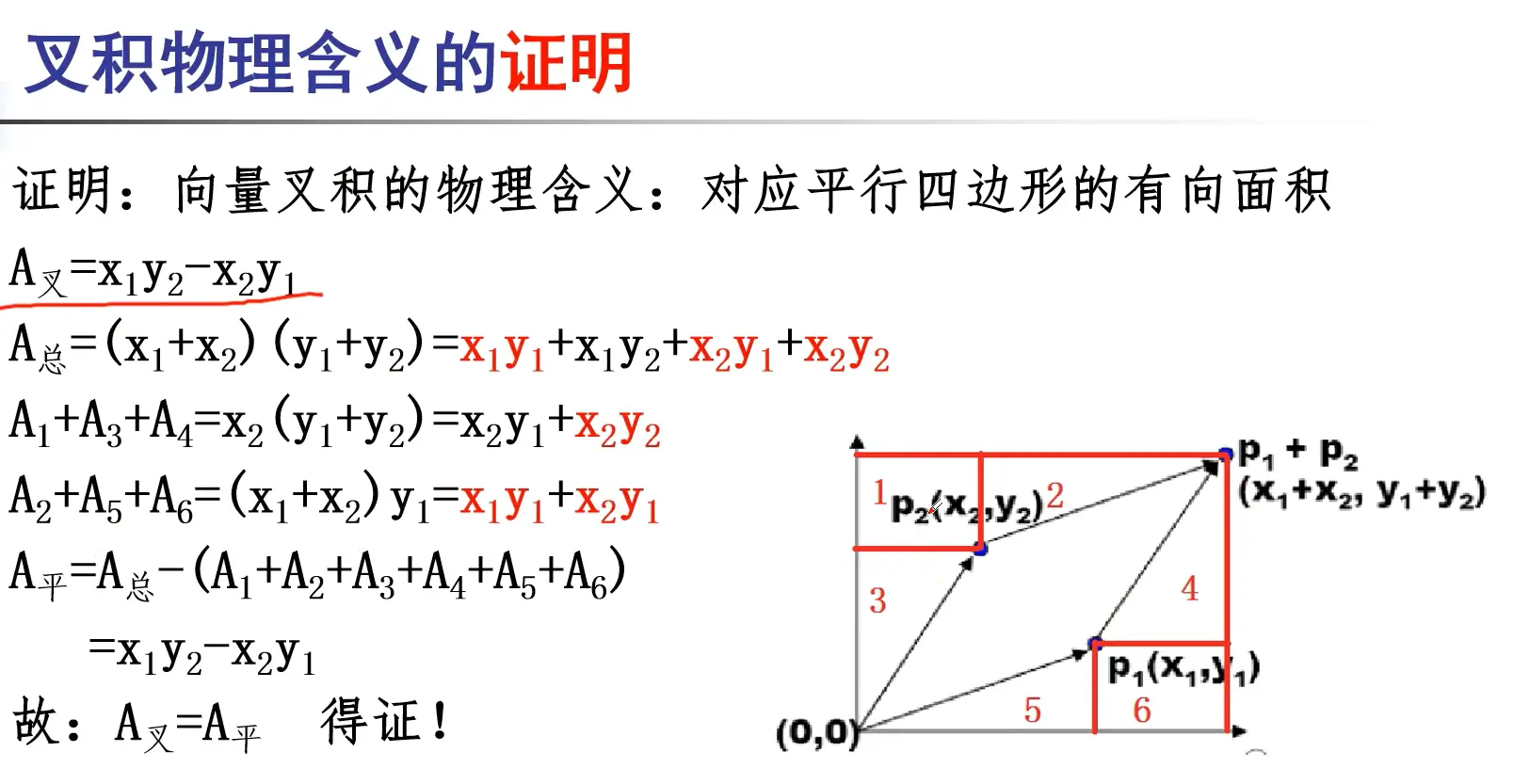
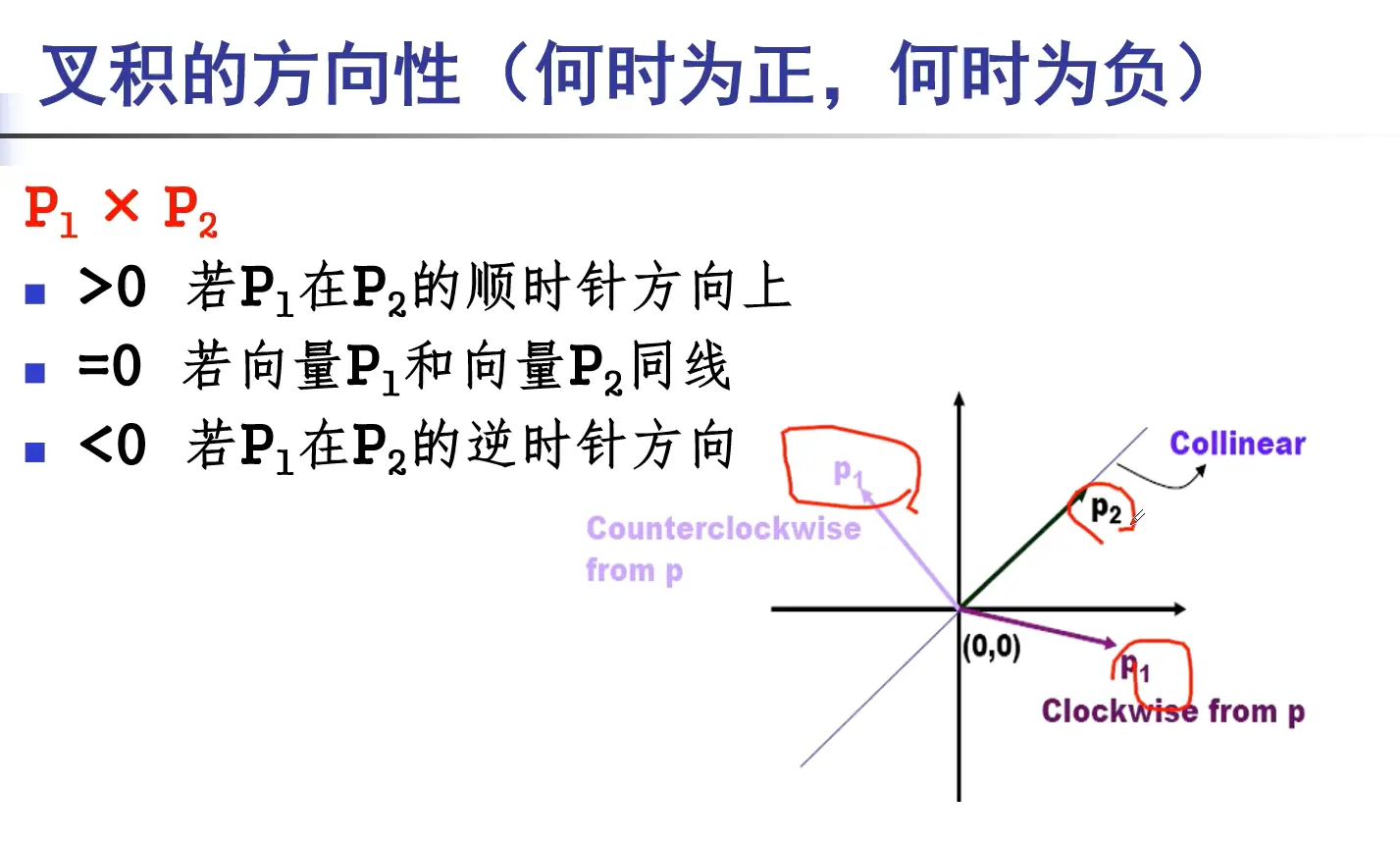
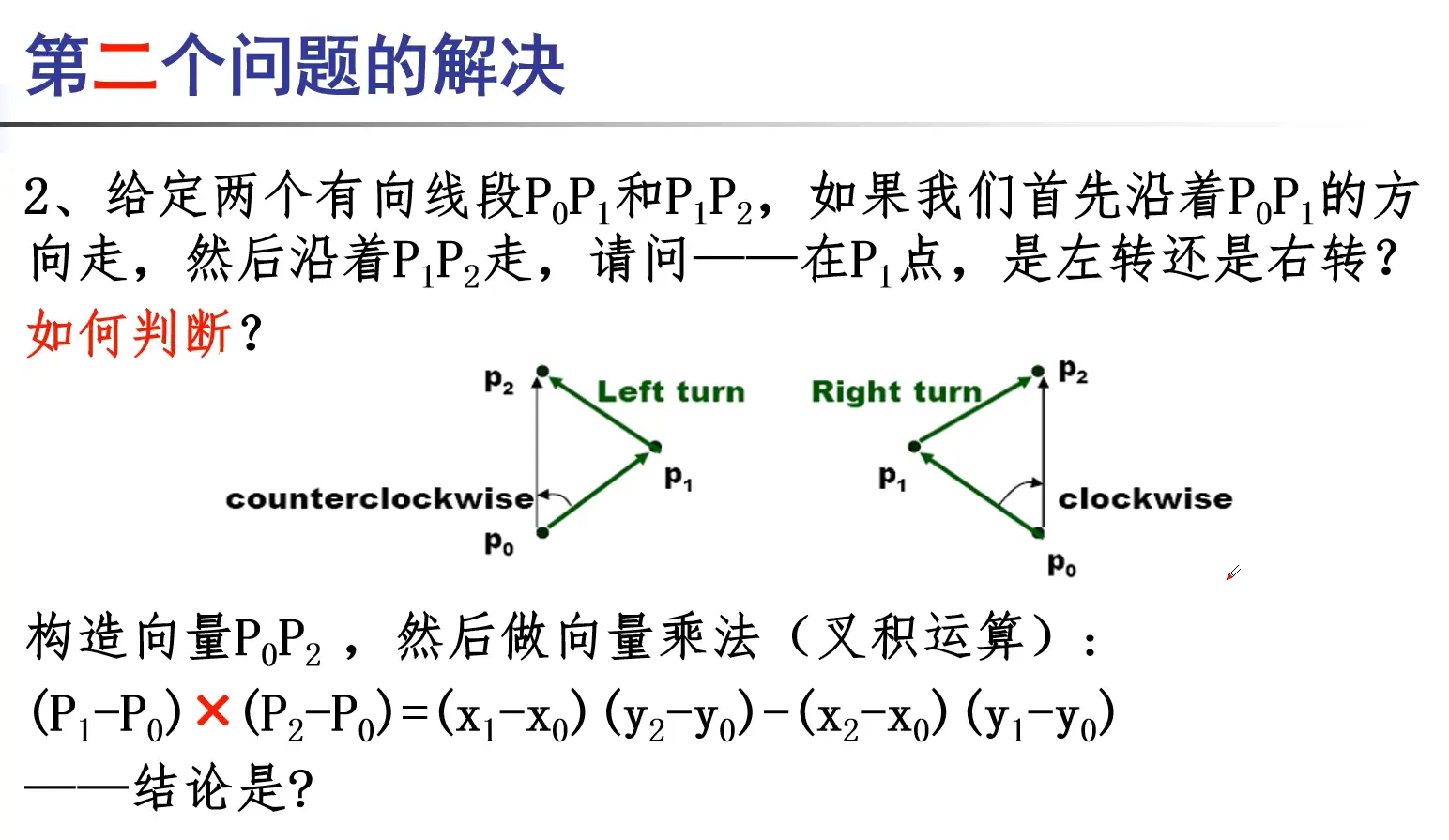
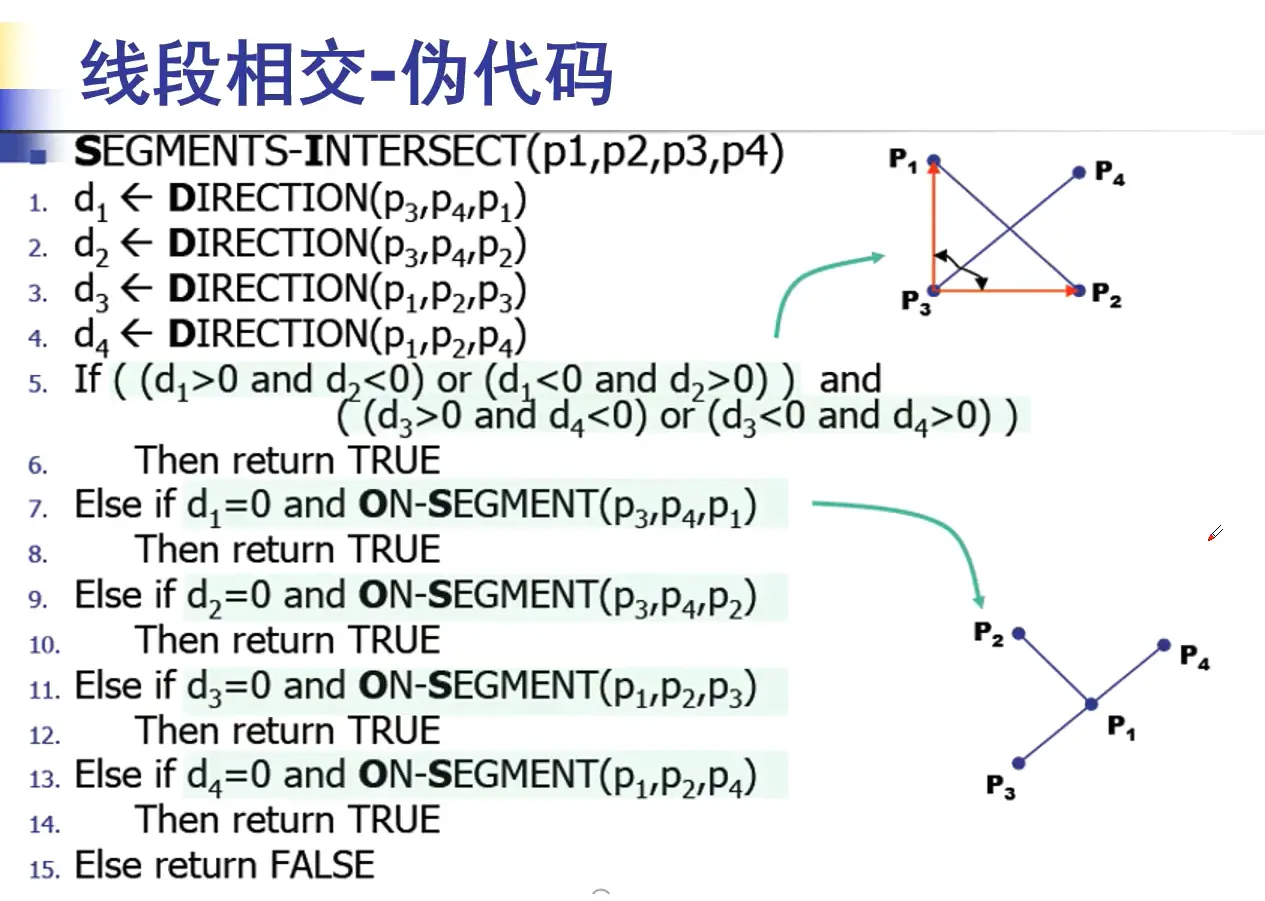
 x,y
都需要判断,这样可以保证垂直,水平下的特殊情况
x,y
都需要判断,这样可以保证垂直,水平下的特殊情况